Introduction
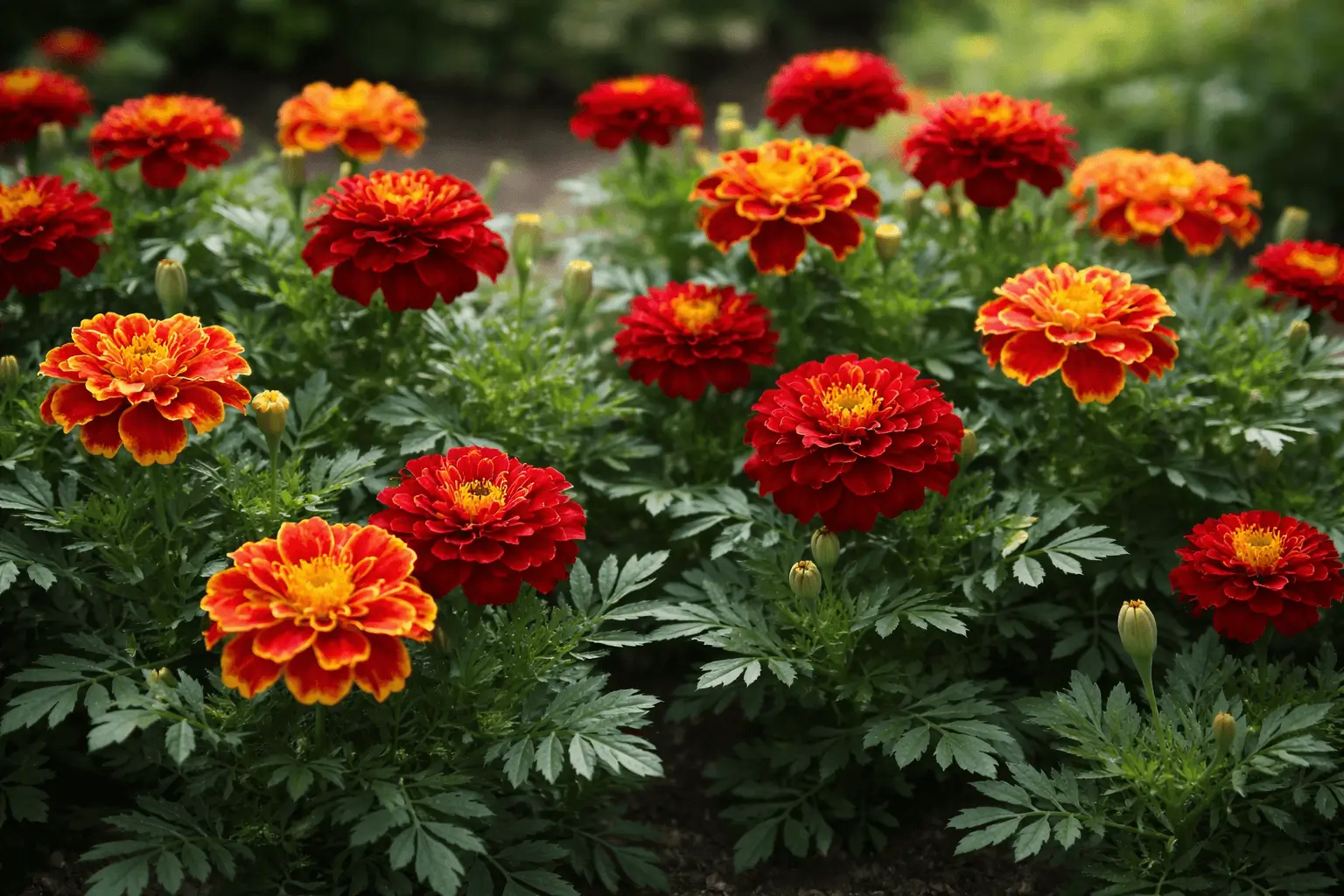
Red marigolds are bold, ornamental flowering plants known for their rich tones, compact growth, and long blooming season. While marigolds are commonly associated with yellow and orange shades, red marigolds stand out due to their deeper hues, bicolor petals, and striking garden contrast. These flowers belong to the Tagetes genus, which includes multiple species and cultivars with wide color variation ranging from pale cream to deep red and mahogany.
A common source of confusion with marigolds is their plant type. Many gardeners are unsure whether marigolds are annual or perennial, as different species behave differently depending on climate and genetics. Understanding this distinction is essential when choosing red marigolds for gardens, borders, or containers.
What Are Red Marigolds?
Marigold Plant Description
Red marigolds are flowering plants from the Asteraceae family, the same plant family as daisies and sunflowers. A typical marigold plant description includes fast-growing habits, aromatic foliage, and dense flower heads. These plants are valued for their adaptability, pest resistance, and vibrant blooms.
Key marigold characteristics include upright or mounded growth, branching stems, and continuous flowering throughout warm seasons. The marigold foliage is usually deep green, finely divided, and slightly fern-like. Each leaf shows a distinct marigold leaf shape, with serrated edges and a strong scent when crushed.
Colours and Appearance of Red Marigolds

Marigolds display a wide spectrum of shades, and the colours of marigolds include yellow, orange, cream, bronze, and red. Red marigolds often appear as solid deep red or as bicolor forms with yellow or orange edges.
In a red and yellow marigolds comparison, red varieties tend to have darker centers and more dramatic contrast, while yellow marigolds appear brighter and more uniform. When asking what does marigold flowers look like, the answer includes layered or simple petals forming rounded, pom-pom-like, or daisy-style blooms depending on the variety.
Types and Varieties of Red Marigolds

Popular Red Marigold Varieties
Several cultivars are recognized for their strong red coloration and garden performance. Each marigold variety differs in size, petal structure, and color intensity.
- Marigold Red Cherry: Compact plants with deep red, velvety blooms
- Mr Majestic marigold: Bicolor flowers with red petals striped in golden yellow
- Star marigold flower: Star-shaped, open blooms with red and orange contrasts
These are commonly grown marigold flower variety selections for borders and pots.
Single vs Double Petal Marigolds
Red marigolds can have either single or double blooms. A single marigold has one row of petals surrounding a visible center, giving it a lighter, more natural look.
- Marigold single petal types attract pollinators more easily
- Single marigold flower forms appear flatter and more open than double types
Double-petaled marigolds, in contrast, have densely packed petals and fuller blooms.
Marigold Species and Classification
Tagetes Species Overview
Most red marigolds are derived from specific tagetes species known for compact size and strong pigmentation. The tagetes marigold flower is typically hardy, fast-growing, and highly floriferous.
The tagetes patula plant, commonly called French marigold, produces many red and bicolor varieties. Its tagetes patula leaves are finely cut and aromatic. In general, tagetes leaves are pinnate, serrated, and deep green.
Tagetes vs Calendula
There is frequent calendula tagetes confusion due to the shared name “marigold.” This distinction is important.
- Tagetes vs calendula: Tagetes are true marigolds; Calendula are pot marigolds
- Pot marigold vs marigold: Calendula belongs to a different genus and has different uses and growth habits
They are not botanically related despite similar appearances.
Are Red Marigolds Annual or Perennial?

Annual Marigolds Explained
Most red marigolds grown in gardens are annual marigolds. These marigold annual flowers complete their entire life cycle in one growing season.
The annual marigolds life cycle includes seed germination, flowering, seed production, and plant death within a year. For most climates, the answer to are marigolds annuals is yes.
Perennial Marigolds Explained
Some species are true perennial marigolds, returning year after year in suitable climates. Gardeners often ask, are marigolds perennial plants, and the answer depends on species.
Examples include:
- Mexican marigold perennial (Tagetes lemmonii)
- Mt Lemmon marigold, a woody perennial species
These survive mild winters and grow as shrubs rather than bedding plants.
How to Tell If a Marigold Is Annual or Perennial
To determine is marigold perennial or annual, observe growth habit and winter survival.
- Woody stems indicate perennial types
- Seed-grown bedding plants are usually annuals
- Research helps confirm are marigolds perennials by species name
Marigold Growth, Size, and Stages
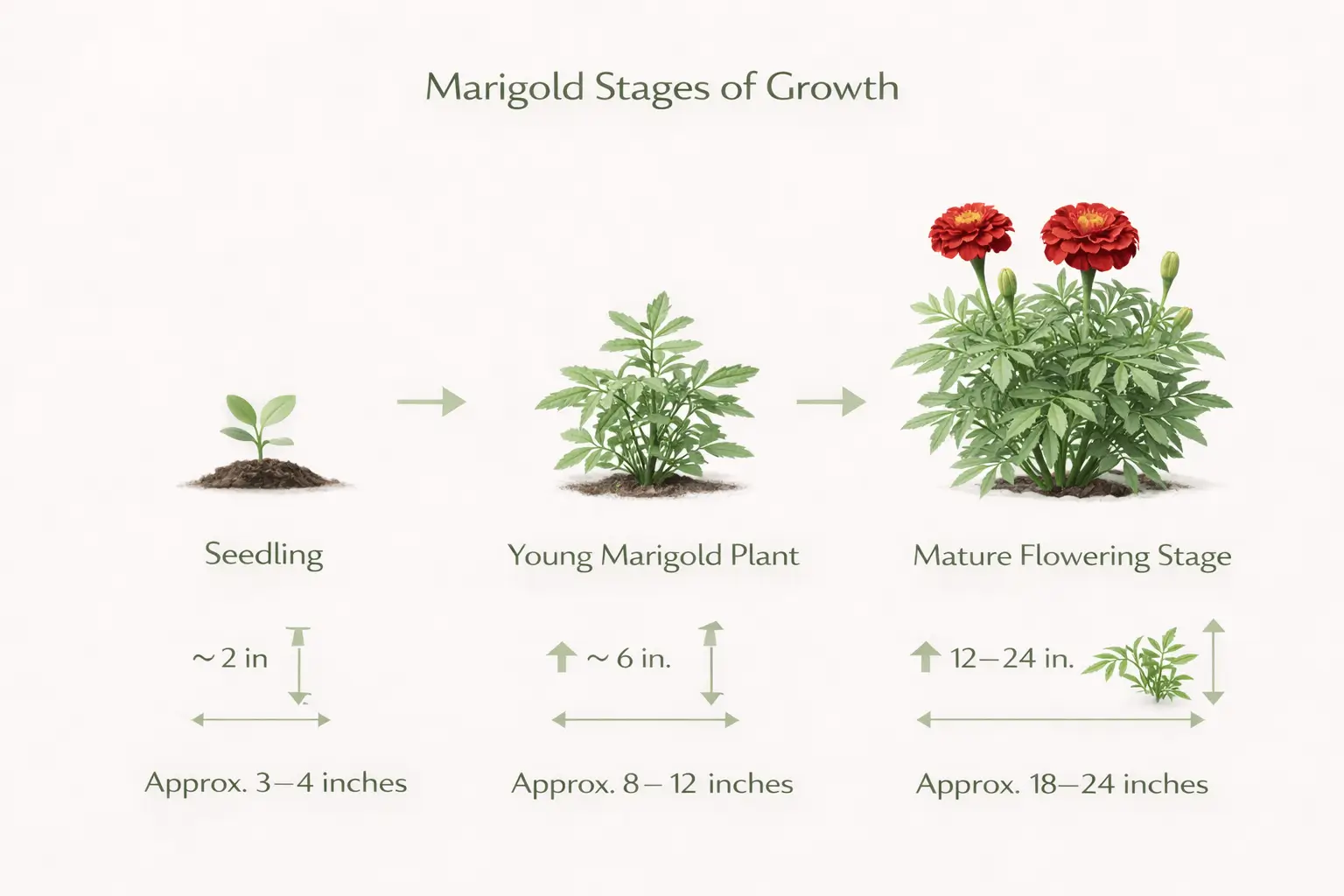
Height and Spread of Marigolds
The height of marigold plants varies by type. Most annual varieties reach 6–18 inches tall.
Typical marigolds height and spread ranges:
- Dwarf types: compact and low-growing
- Medium types: wider spread with bushy form
Marigold Growth Stages
Understanding marigold stages of growth helps with care timing. A gardener may wonder, what does marigold seedling look like—it appears as a small, upright sprout with narrow initial leaves.
Young marigold plants quickly enter the sprouting phase, followed by branching and bud formation.
Hardiness and Climate Tolerance of Red Marigolds
Marigold Hardiness and Zones
Many gardeners ask, how hardy are marigolds. Most red marigolds are warm-season plants.
The typical marigold hardiness zone suitability is USDA zones 2–11 as annuals. In general, are marigolds hardy depends on temperature rather than soil.
Cold and Frost Tolerance
Marigold frost tolerance is low. Even light frost can damage plants.
- Marigold cold hardiness is limited
- Marigolds cold hardy only in frost-free climates
Basic Care Requirements for Red Marigolds
Light Requirements
The ideal light requirements for marigold plants include full sun. At least 6 hours of direct sunlight promotes dense growth and deep flower color.
Caring for Marigold Plants
Basic caring for marigold plants includes:
- Moderate watering with well-drained soil
- Proper spacing when planting marigolds to plant in beds or pots
- Minimal feeding for continuous blooms
Edibility and Uses of Marigolds
Are Red Marigolds Edible?
Gardeners often ask, are all marigolds edible. Only certain species are safe for consumption.
- Edible marigold varieties are typically from Calendula, not Tagetes
- Knowing marigold edible or not depends on species
- Some which marigolds are not edible types can be bitter or unsafe
Red marigolds grown for ornament are generally not used as edible flowers.
Conclusion
Red marigolds offer a wide range of visual styles, growth habits, and plant types, making them a versatile choice for home gardens and containers. From compact annual bedding plants like Red Cherry and Mr Majestic to woody perennial species such as Mexican marigold, red marigolds vary greatly in form and lifespan. Most commonly grown red marigolds are annuals, valued for fast growth, heavy blooming, and ease of care.
Choosing the right marigold depends on climate, space, and intended use. Garden beds benefit from spreading annual varieties, while pots and borders suit compact or dwarf types. In warmer regions, perennial marigolds provide long-term structure. Selecting the correct type ensures healthier plants, better flowering, and long-lasting garden performance.
Read Also: 7+ Expert Secrets to Grow Anthurium Vittarifolium
FAQs
Are red marigolds annual or perennial?
Most red marigolds grown in gardens are annuals that complete their life cycle in one season. However, a few species, such as Mexican marigold and Mt Lemmon marigold, are true perennials in warm climates.
How hardy are red marigolds in cold climates?
Red marigolds are not frost tolerant. Annual varieties die with the first frost, while perennial marigolds survive only in mild, frost-free regions. In cold climates, they are grown strictly as summer annuals.
Which red marigold varieties grow best in pots?
Compact varieties such as Red Cherry marigold and Mr Majestic marigold perform best in containers. These types have controlled growth, strong branching, and consistent flowering in limited space.
Are red marigolds edible?
Most red marigolds from the Tagetes genus are not considered edible and may have a bitter taste. Edible marigolds are usually Calendula varieties, which are botanically different from ornamental red marigolds.
How tall do red marigold plants grow?
Red marigold height varies by variety. Dwarf types grow 6–10 inches tall, medium varieties reach 12–18 inches, and perennial marigolds can grow several feet tall in favorable climates.




